The impact of human activity on the environment is becoming increasingly apparent. In light of this, the need for sustainable practices has never been more urgent. One crucial aspect of this shift towards sustainability is rethinking how we get from place to place. Typical modes of transportation, those powered by fossil fuels, have long been a major contributor to environmental degradation and public health issues. However, the concept of “green transportation” offers us a solution to these evolving challenges.
Green transportation refers to modes of transportation that prioritize environmental sustainability and minimize negative impacts on the environment. Unlike conventional transportation methods that rely heavily on fossil fuels and produce problematic emissions, green transportation embraces alternative energy sources and promotes efficiency and conservation.
The importance of adopting green transportation methods cannot be overstated. With air and water pollution reaching alarming levels across the globe, transitioning to more sustainable modes of transportation is essential in protecting both environmental and public health. By reducing emissions and reliance on finite resources, green transportation can play a vital role in mitigating pollution, improving air quality, and preserving natural habitats.
In this piece, we will explore the various aspects of green transportation, from its environmental and health benefits to the different types of sustainable transportation options available. We will look into the challenges and barriers facing the widespread adoption of green transportation, as well as highlight solutions and offer some practical tips for people looking to make greener transportation choices.
The Problem with Conventional Transportation
Environmental Impacts
Conventional transportation, primarily fueled by gasoline and diesel, poses significant environmental challenges. The combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles releases pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. These pollutants contribute to air pollution, smog formation, and the exacerbation of climate change.
Health Implications of Air Pollution and Emissions
The harmful effects of air pollution on human health are well-documented. Exposure to pollutants emitted by vehicles has been linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular disorders, and even premature death. Vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly at risk. To make things worse, air pollution from transportation has similarly negative impacts on ecosystems, wildlife, and agricultural productivity.
Dependency on Finite Fuels
Conventional transportation systems are heavily reliant on fossil fuels that are non-renewable resources, such as oil and natural gas. The extraction, processing, and combustion of fossil fuels not only contribute to environmental degradation but also tend to be a major driver of geopolitical tensions and economic volatility. As global demand for transportation continues to rise as the population grows, the depletion of fossil fuel reserves poses a looming threat to energy security and economic health.
Benefits of Green Transportation
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The adoption of green transportation methods significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike conventional vehicles powered by gasoline or diesel, green transportation options such as electric vehicles (EVs), public transportation, cycling, and walking produce fewer or zero emissions during operation. By transitioning to cleaner energy sources and more efficient transportation systems, we can curb our carbon footprint and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Improved Air Quality and Public Health
One of the most immediate and tangible benefits of green transportation is the improvement of air quality and public health. By reducing emissions of harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), green transportation helps to reduce smog formation and respiratory ailments. Cleaner air naturally yields healthier communities, lower healthcare costs, and enhanced quality of life for residents, particularly in densely populated urban areas with heavy traffic.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Green transportation also contributes to the conservation of natural resources, including fossil fuels and ecosystems. By shifting away from fossil fuel-dependent vehicles, we can reduce our dependence on limited resources and minimize the environmental impacts associated with resource extraction, refining, and transportation. Promoting other modes of transportation like biking and walking also helps to preserve our green spaces, biodiversity, and wildlife habitats.
Economic Benefits and Cost Savings
In addition to the more obvious environmental and health advantages, green transportation can also offer significant economic benefits and cost savings for people. While the upfront costs of purchasing electric vehicles or investing in public transportation infrastructure can seem daunting or inconvenient, the long-term savings in fuel and vehicle maintenance expenses can outweigh these initial investments. Also, as we develop sustainable transportation systems, we create job opportunities in industries such as renewable energy, public transit, and urban planning, stimulating economic growth and innovation.
By embracing green transportation solutions, we can all enjoy a ton of benefits for both people and the planet.
Types of Green Transportation
The term”green transportation” can be used to encompass a wide variety of solutions, but generally, the term is used to describe all modes of transportation that aim to minimize environmental impact and promote energy efficiency. Here are some of the major types of green transportation:
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) are powered by rechargeable batteries and electric motors, eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, which offer a massive reduction of air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. EVs come in a few different forms, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). As battery technology advances and charging infrastructure expands, EVs are becoming increasingly accessible and practical, though the technology still needs more development for its full potential to be realized.
Public Transportation
Public transportation systems like buses, trains, trams, and subways do a lot to cut down on traffic congestion and emissions in urban areas. By providing an alternative to individual car trips, public transit helps to improve air quality, decrease energy consumption, and enhance mobility for a wide range of populations. Investments in expanding and improving public transportation infrastructure are needed to encourage more widespread use and reduce reliance on individual vehicles, but there is certainly a lot of potential in this area.
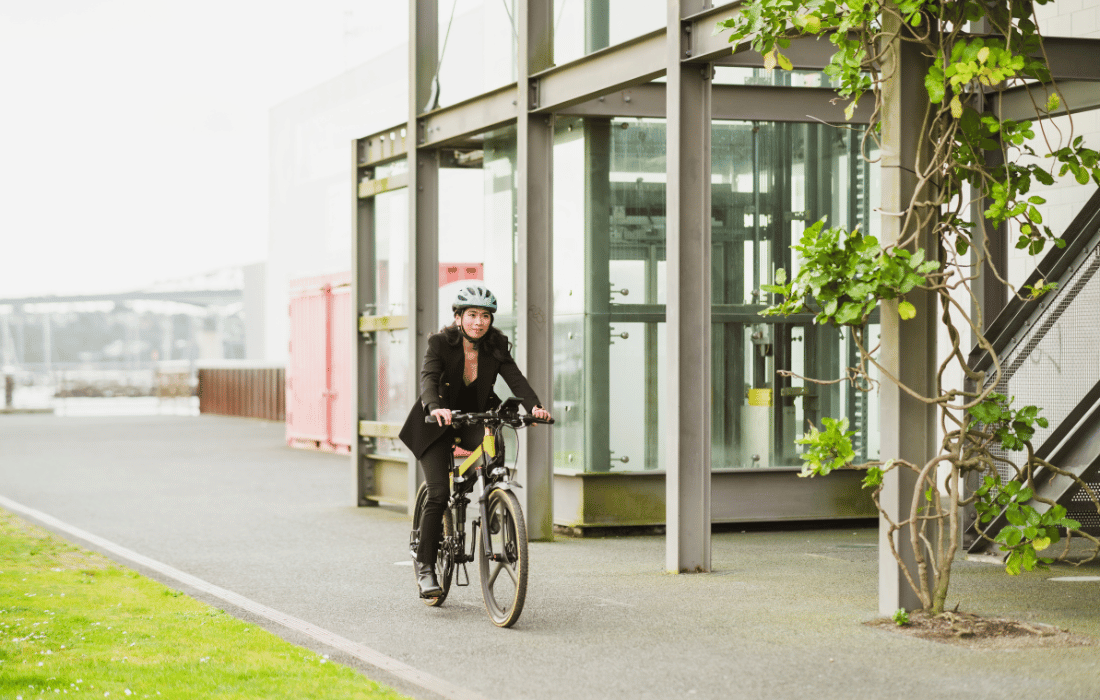
Cycling and Walking
Cycling and walking are the OG emissions-free modes of transportation that offer numerous health, environmental, and economic benefits. By choosing to cycle or walk for short trips instead of driving, individuals can reduce carbon emissions, hugely improve their physical fitness, and save money on transportation costs. Investing in cycling infrastructure, such as bike lanes, bike-sharing programs, and pedestrian-friendly pathways, can do a lot to encourage more people to embrace active transportation and contribute to creating safer and more livable communities — European cities like Copenhagen and Amsterdam stand as incredible examples of what a cycle and walking friendly city can look like.
Alternative Fuels
In addition to electric vehicles, alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, hydrogen, and compressed natural gas (CNG) offer cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to conventional gasoline and diesel. These fuels can be produced from renewable sources such as plant biomass or agricultural waste, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing overall environmental impact. While infrastructure and technology for alternative fuels are still evolving, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for greater adoption and integration into the transportation sector.
Challenges and Barriers
While green transportation offers many potential benefits, there are also some significant hurdles to furthering adoption:
- Infrastructure Challenges: One of the primary challenges facing green transportation is the lack of adequate infrastructure to support these alternative modes of transportation. For electric vehicles, there is a lack of charging stations and grid capacity to meet increased demand. Similarly, bike lanes and sidewalks are poorly maintained or simply not present in many areas.
- Affordability and Accessibility: The upfront costs of purchasing electric vehicles or investing in alternative transportation options can be a major barrier for many individuals who would otherwise consider the transition, particularly those with limited financial resources. Access to public transportation services and cycling infrastructure tends to disproportionately affect marginalized communities, exacerbating transportation issues.
- Psychological Barriers: Many people are simply using to relying on their cars for convenience and comfort; transitioning to alternative modes of transportation can feel limiting and inconvenient for many, particularly in areas where public transportation infrastructure is lacking.
- Political and Regulatory Complexities: Political and regulatory factors, including lack of political will, inconsistent policies, and financial interests, can slow progress toward sustainable transportation solutions. It is not uncommon that vested interests in the fossil fuel industry and automotive sector resist efforts to promote alternatives.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and communities to create a supportive environment for green transportation adoption.
Tips for More Sustainable Transportation
Transitioning to green transportation doesn’t have to be a hassle and can actually bring a lot of enrichment to your life. Here are some tips to help you get there:
- Choose Sustainable Modes of Transportation: This one seems obvious, but it’s a big one… choose! You do have a lot of say in how things play out and conscious choice plays a big role in that. Opt for walking, cycling, or taking public transit whenever you can. These forms of transportation produce significantly fewer emissions and promote physical activity, leading to improved health and well-being.
- Carpooling and Ride-Sharing: Sharing rides with friends, family, or coworkers reduces the number of vehicles on the road and minimizes carbon emissions. Carpooling and ride-sharing services offer convenient alternatives to driving alone and can save money on fuel, parking, etc.
- Consider an Electric Vehicle: If feasible, consider switching to an electric vehicle (EV) for your daily commute or transportation needs. You will drastically reduce your carbon footprint and support innovation that could change the world as the technology continues to develop.
- Support Sustainable Transportation Infrastructure: Advocate for investments in cycling infrastructure, public transit expansion, and electric vehicle charging networks in your community. Participate in local planning and ask your elected officials to prioritize sustainable transportation projects.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Knowledge is power! Stay informed about the benefits of green transportation and share your knowledge with your community. Encourage friends, family, and colleagues to join you in adopting more sustainable transportation practices.
By incorporating these tips into your lifestyle and advocating for sustainable transportation solutions, you can do your part to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and build more enjoyable and resilient communities for current and future generations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, green transportation presents a hopeful solution to the environmental, health, and economic challenges posed by conventional transportation systems. By prioritizing sustainability, efficiency, and innovation, we can transition towards transportation options that minimize emissions, reduce dependence on non-renewable resources, and enhance the quality of life for all.
Throughout this blog, we’ve explored the benefits of green transportation, including improved air quality, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and cost savings. We’ve also discussed the various types of green transportation, from electric vehicles and public transit to cycling and walking, as well as the challenges and barriers to their widespread adoption.
Despite the challenges, there is a lot that we can do as a collective to promote sustainable transportation at the local, national, and global levels. By implementing government policies, corporate initiatives, community-based programs, and technological advancements, we can overcome obstacles and accelerate the development of greener transportation systems.
As individuals, we can also make a difference by adopting sustainable transportation practices in our daily lives, whether it’s choosing alternative modes of transportation, supporting green infrastructure investments, or advocating for policy changes in our communities.
By working together to do our best, we can create a future where transportation is not only efficient and accessible but also environmentally friendly and equitable. Let’s continue to drive progress towards a more sustainable and resilient transportation system for generations to come.