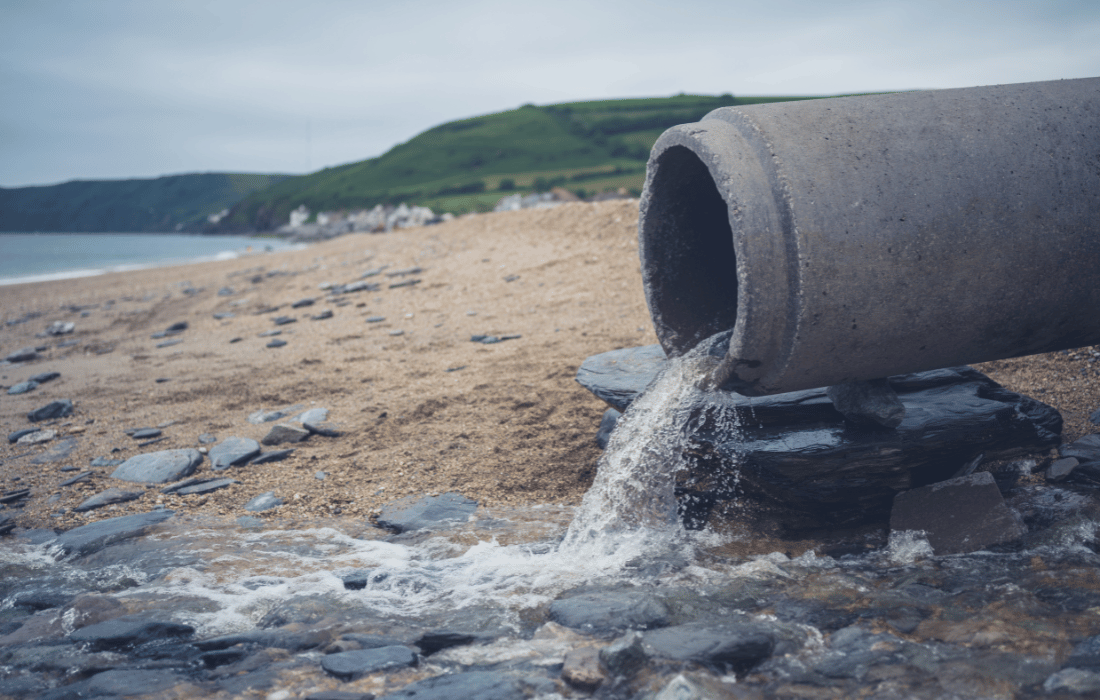
On a sunny day in May, the idyllic shores of Venice Beach were overshadowed by an environmental crisis as a roughly two-mile stretch of coastline in the Marina del Rey and Playa del Rey areas was closed due to a sewage spill. The incident, which occurred between Wednesday, May 8th, and midday Thursday, May 9th, saw approximately 14,400 gallons of untreated sewage flow into Ballona Creek, ultimately discharging into the ocean.
The spill, of which the source has yet to be disclosed, has prompted swift action from the county Department of Public Health. Health officials issued a closure order, urging the public to steer clear of the ocean water and any wet sand within one mile north and south of Ballona Creek. This closure encompassed an extensive area, stretching from the southern end of Venice Beach through the Marina del Rey area and south to Dockweiler State Beach.
“The Department of Public Health will conduct water sampling beginning (Friday), and the closures will remain in effect until Public Health receives two sampling results indicating that bacteria levels meet health standards,” stated the agency.
This incident underscores the critical importance of addressing environmental health issues promptly and effectively. Sewage spills represent a serious threat to both public health and marine ecosystems, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to safeguard our environment and well-being.
In this blog post, we’ll review the Ballona Creek sewage spill and the potential causes and consequences. We will explore the environmental impact of sewage spills on marine ecosystems, as well as the public health risks associated with exposure to contaminated water. Additionally, we will discuss the response and cleanup efforts underway, highlighting the importance of community engagement and awareness in mitigating the effects of such environmental disasters.
Join us in shedding some light on the urgent need for sustainable solutions to protect our environment and public health.
Background Information
The sewage spill that has tainted the idyllic beaches of Venice Beach and Playa Del Rey, highlights the urgent need for a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to such environmental disasters. This is also not the first event like this in the area — in July of 2021, an estimated 17,000,000 gallons of untreated sewage spilled from the Hyperion Water Reclamation Plant into Santa Monica Bay.
Sewage spills are often the result of failures within wastewater infrastructure systems. Aging pipes, insufficient maintenance, and capacity issues can all contribute to the vulnerability of these systems, particularly during periods of heavy rainfall or increased demand. In the case of the Ballona Creek incident, the precise source of the spill has yet to be disclosed as we write this the following week, leaving the public awaiting authorities and environmental experts to investigate the root cause.
The environmental impact of sewage spills extends far beyond the immediate vicinity of the incident. Untreated sewage contains a cocktail of harmful contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, and chemicals, which can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems. From disrupting delicate aquatic habitats to contaminating recreational waters, sewage spills pose significant risks to both marine life and human health.
This Southern California incident serves as a sobering reminder of the systemic challenges facing wastewater management systems, not only in California but across the globe. As urbanization continues to increase pressure on aging infrastructure and climate change exacerbates the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, the risk of sewage spills looms large.
Environmental Impact
The Balonna Creek sewage spill has unleashed a cascade of environmental consequences, reverberating throughout the delicate ecosystems of the affected area. Understanding the extent of these impacts is crucial for assessing the long-term ramifications and guiding effective mitigation efforts.
Water Quality
The primary concern following a sewage spill is, obviously, the compromised quality of water in the affected area. Untreated sewage introduces a plethora of pollutants, including bacteria, viruses, and toxic chemicals, into the waterways. These contaminants not only pose immediate health risks to humans but also degrade water quality, making it unsuitable for marine life. As a result, the spill has triggered widespread water quality advisories, warning residents and visitors to avoid all contact with contaminated water.
Marine Life
The marine ecosystems surrounding Playa del Rey and Venice Beach are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of sewage spills. Aquatic organisms, ranging from microscopic plankton to larger fish and marine mammals, are directly exposed to harmful pollutants released into their habitats. The presence of pathogens and toxins can lead to widespread mortality among marine life, disrupt food chains, and impair the reproductive success of species. Additionally, the spill may result in the formation of harmful algal blooms, further exacerbating ecological imbalances and threatening the health of marine ecosystems.
Ecosystem Resilience
The resilience of the affected ecosystems in the area will play a critical role in determining their ability to recover from sewage spills. While some species may exhibit resilience to short-term disturbances, others may face long-lasting impacts, particularly if exposed to high levels of pollutants or habitat degradation. Monitoring the health and recovery of marine ecosystems in the aftermath of the spill is essential for assessing the effectiveness of cleanup efforts and implementing targeted restoration measures.
Public Health Concerns
In addition to the more obvious environmental concerns, the sewage spill also presents significant public health risks, with potential consequences for both beachgoers and residents in the affected areas. Understanding these risks is paramount for ensuring the safety and well-being of the community in the aftermath of the spill.
Risks of Exposure
Exposure to sewage-contaminated water poses numerous health hazards, including bacterial and viral infections, gastrointestinal illnesses, and skin irritations. Beachgoers who come into direct contact with contaminated water or wet sand may unknowingly expose themselves to pathogens, increasing the likelihood of illness. Additionally, inhalation of contaminated aerosols or ingestion of contaminated water during recreational activities such as swimming or surfing can further heighten the risk of infection.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain demographic groups, such as children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with compromised immune systems, are particularly susceptible to the health effects of sewage exposure. Children, in particular, may be at greater risk due to their tendency to play in the sand and shallow water, where contamination levels may be higher. Pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals should also exercise caution to avoid potential health complications associated with sewage exposure.
Long-Term Health Impacts
While the immediate health effects of sewage exposure may manifest as acute illnesses, the long-term health impacts can be equally concerning. Chronic exposure to sewage-contaminated water may increase the risk of developing respiratory infections, gastrointestinal disorders, and other health conditions over time. Additionally, repeated incidents of sewage spills can erode public trust in water quality and undermine community well-being, highlighting the importance of proactive measures to prevent future occurrences.
In light of these public health concerns, authorities and health officials have issued advisories urging residents and visitors to avoid contact with contaminated water and adhere to safety precautions until water quality standards are restored.
Response and Current Efforts
In the aftermath of the Ballona Creek sewage spill, immediate actions have been taken to assess the extent of contamination and safeguard public health. While cleanup efforts have yet to commence, water quality monitoring programs have been implemented to track the presence of contaminants and inform decision-making regarding beach closures and safety advisories.
Water Quality Testing
Following the discovery of the sewage spill, authorities swiftly initiated water quality testing to assess the level of contamination in the affected area. Samples of water and sediment have been collected at regular intervals from various locations within the vicinity of the spill for laboratory analysis. These tests aim to identify indicators of sewage contamination, such as fecal coliform bacteria and chemical pollutants, to evaluate the potential risks to public health.
Beach Closures and Safety Advisories
Based on the results of water quality testing, health officials have issued beach closures and safety advisories to minimize the risk of exposure to contaminated water. Public announcements and signage have been deployed to notify residents and visitors of the closures and urge compliance with safety precautions. These measures are essential for protecting the health and well-being of beachgoers and reducing the likelihood of waterborne illnesses.
Collaboration and Coordination
While cleanup efforts have yet to commence, collaborative efforts between government agencies, environmental organizations, and community stakeholders will be essential to coordinate a comprehensive response. Ongoing communication and collaboration are vital for ensuring a unified and effective response to the sewage spill and minimizing its impact on public health and the environment.
As authorities continue to monitor water quality and assess the situation in the Playa del Rey and Venice Beach areas, the community must remain vigilant and adhere to safety advisories to mitigate the risks associated with sewage contamination. While the road to recovery and prevention of such events may be challenging, collective action and cooperation will be essential for restoring the affected environment and safeguarding the health of residents and visitors moving forward.
Conclusion
The recent sewage spill that has blanketed Playa del Rey and Venice Beach underscores the urgent need to address environmental health issues promptly and effectively. This incident, occurring between May 8th and May 9th, resulted in extensive beach closures and safety advisories issued by the county Department of Public Health.
Sewage spills continue to pose significant risks to both marine ecosystems and public health. Aging infrastructure and capacity issues contribute to the vulnerability of wastewater management systems, exacerbating the risk of environmental disasters like the one currently being witnessed in the Venice Beach area.
While cleanup efforts have yet to commence, rigorous water quality testing and public health advisories have been implemented to assess contamination levels and minimize risks to the community. Ongoing collaboration between government agencies, environmental organizations, and community stakeholders will be imperative for coordinating response efforts and restoring the affected environment.
As we reflect on the challenges posed by the recent sewage spill, it is clear that collective action and cooperation are essential for addressing environmental health issues and promoting sustainable solutions. By raising awareness, advocating for improved infrastructure, and fostering community engagement, we can work together to protect our environment and public health for generations to come.