For decades, creatine has been a staple in the world of sports nutrition, though it’s mostly been associated with athletes – mostly guys – looking to build muscle and enhance their strength. Interestingly though, emerging research suggests that creatine might be one of the most underrated supplements for women, athletes, and nonathletes alike. From improving physical performance to supporting brain function, hormonal balance, and even mental health, creatine has a lot to offer women across all stages of life.
Despite its wide use and extensive research, the unique benefits of creatine for females remain pretty under-discussed. Women naturally have lower creatine stores than men, and their dietary intake is often significantly lower. This suggests that women may benefit even more from supplementation than guys would, yet misconceptions about weight gain and side effects have prevented so many ladies from tapping into creatine’s potential. We hope to change that today.
How Creatine Works in the Body
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that helps produce ATP – the body’s primary energy currency. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides the energy to drive and support many processes in living cells like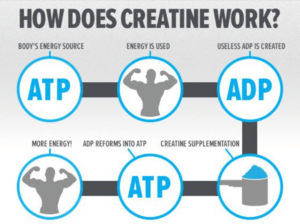 muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Creatine plays a vital role in maintaining muscle energy levels, buffering pH balance, and supporting neural function. While creatine is mostly recognized for its role in exercise performance, its presence in the brain, muscles, and even bones suggests far-reaching benefits beyond just athletic performance.
muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Creatine plays a vital role in maintaining muscle energy levels, buffering pH balance, and supporting neural function. While creatine is mostly recognized for its role in exercise performance, its presence in the brain, muscles, and even bones suggests far-reaching benefits beyond just athletic performance.
Creatine Across a Woman’s Lifespan
Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life impact creatine metabolism. Menstrual cycles, puberty, pregnancy, postpartum recovery, perimenopause, and menopause all bring significant metabolic and physiological changes that creatine may help balance.
Menstrual Cycle
Estrogen influences creatine metabolism. Research suggests that creatine kinase levels fluctuate with estrogen levels, peaking during the luteal phase (high estrogen) and dropping during the follicular phase (low estrogen). This makes supplementation particularly relevant for women dealing with low energy, increased fatigue, or poor exercise recovery during certain parts of their cycle.
Pregnancy and Postpartum
The body’s demand for creatine rises during pregnancy due to fetal development and increased metabolic activity. Low creatine levels have been linked to poor fetal growth and preterm birth.
Research suggests creatine supplementation could support fetal brain development and reduce birth complications.
Perimenopause
During this time, women often experience increased fatigue, brain fog, and a decline in muscle strength due to hormonal shifts and a natural decrease in creatine stores. Since estrogen plays a role in creatine metabolism, its decline during perimenopause may lead to reduced cellular energy production and impaired recovery from physical and mental stress. Supplementing with creatine during perimenopause can help counteract these effects by supporting muscle preservation, improving cognitive function, and enhancing energy production.
Menopause
Estrogen plays a critical role in muscle and bone maintenance. As estrogen declines post-menopause, women experience muscle loss, increased inflammation, and reduced bone density. Creatine has been shown to counteract these effects by improving muscle mass, strength, and even bone health.
It should also be noted that creatine has been shown to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress – both of which contribute to accelerated aging and increased risk of metabolic disorders during perimenopause and menopause. By maintaining optimal creatine levels, women can gain improved strength, mental clarity, and overall resilience, making it a powerful ally for navigating these taxing life transitions.
Creatine for Performance and Recovery
The main reason most people supplement with creatine is for athletic performance – and it works exceptionally well for women. Contrary to popular belief, creatine does not cause significant weight gain in women, and any “bloating” it does cause is typically only in the initial loading phase because it increases water retention in muscles. Creatine’s primary effects are that it will enhance strength, power, and endurance during workouts and strength training.
Scientific data consistently shows that creatine supplementation:
- Improves strength and power output during resistance training.
- Enhances muscle recovery and reduces soreness.
- Increases anaerobic performance, such as sprinting and jumping.
- Helps maintain muscle mass even during periods of detraining or inactivity.
Creatine also plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in preserving lean muscle mass during periods of caloric restriction. This makes it an excellent supplement for women who engage in intermittent fasting, endurance training, or those who are trying to maintain muscle while losing fat.
Creatine for Brain Health and Mood
One of the most exciting areas of creatine research is its impact on brain function. Since the brain is a such a high-energy organ, creatine plays a role in cognitive performance, mental clarity, and mood regulation.
Depression and Mental Health
Women are twice as likely as men to experience – or at least be diagnosed with – depression, particularly during hormonal transitions such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, postpartum, perimenopause and menopause. Research has shown that creatine supplementation can enhance the effectiveness of brain boosting supplements and antidepressant medications, likely due to its role in energy metabolism in the brain.
metabolism in the brain.
Cognition and Memory
Creatine has been linked to improved memory, mental clarity, and overall cognitive function. This is particularly beneficial for women dealing with brain fog, stress, or sleep deprivation.
Sleep and Fatigue
Sleep deprivation tends to impact women more severely than men, leading to greater cognitive impairment and slower recovery. Studies suggest creatine may help mitigate the negative effects of sleep loss by supporting ATP production in the brain.
Creatine’s Synergy with Other Supplements
Creatine works even better when paired with other supportive nutrients. Some of the best combinations include:
- Creatine + Protein: While creatine supports energy production, protein provides the necessary building blocks for muscle repair and growth.
- Creatine + Magnesium: Magnesium is crucial for ATP metabolism and can enhance creatine absorption.
- Creatine + Collagen: This duo can be particularly beneficial for women looking to support joint, skin, and connective tissue health while also maintaining muscle mass.
Dosing and Usage Tips
For women, the most effective dosing strategy is:
- Loading Phase (optional): 20g per day (split into 4 doses) for 5-7 days.
- Maintenance Phase: 3-5g per day for long-term use.
Women who want to avoid the loading phase and some of the potential water retention can simply start with 3-5g per day and allow their creatine stores to gradually build up over a few weeks.
Incorporating Creatine Into Your Routine
Creatine is flavorless and dissolves easily in water, smoothies, or other beverages. Here are some simple ways to include it in your daily routine:
- Morning routine: Mix 3-5g into your coffee, tea, or smoothie. It should be noted that creatine used to be suggested to be taken separately from caffeine, but it’s been mostly proven that it has little to no effect on the performance and efficacy of either supplement.
- Pre/Post-Workout: Add it to your pre-workout drink or post-workout protein shake.
- Before bed: Some women find creatine beneficial when taken before sleep, particularly for muscle recovery and cognitive support.
Closing Thoughts
Creatine is more than just a sports supplement for gym-rat dudes – it’s a powerful tool for enhancing overall health, performance, and longevity in women. Whether it’s supporting energy levels during workouts, promoting cognitive function, easing symptoms during hormonal shifts, or aiding in muscle maintenance, creatine deserves a place in the conversation around female health and wellness. It may be one of the most underrated supplements for women today.